Did One Man's Experiment Revolutionize Farming? The Story of Crop Rotation
Discover the Revolutionary Farming Experiment That Changed Agriculture Forever
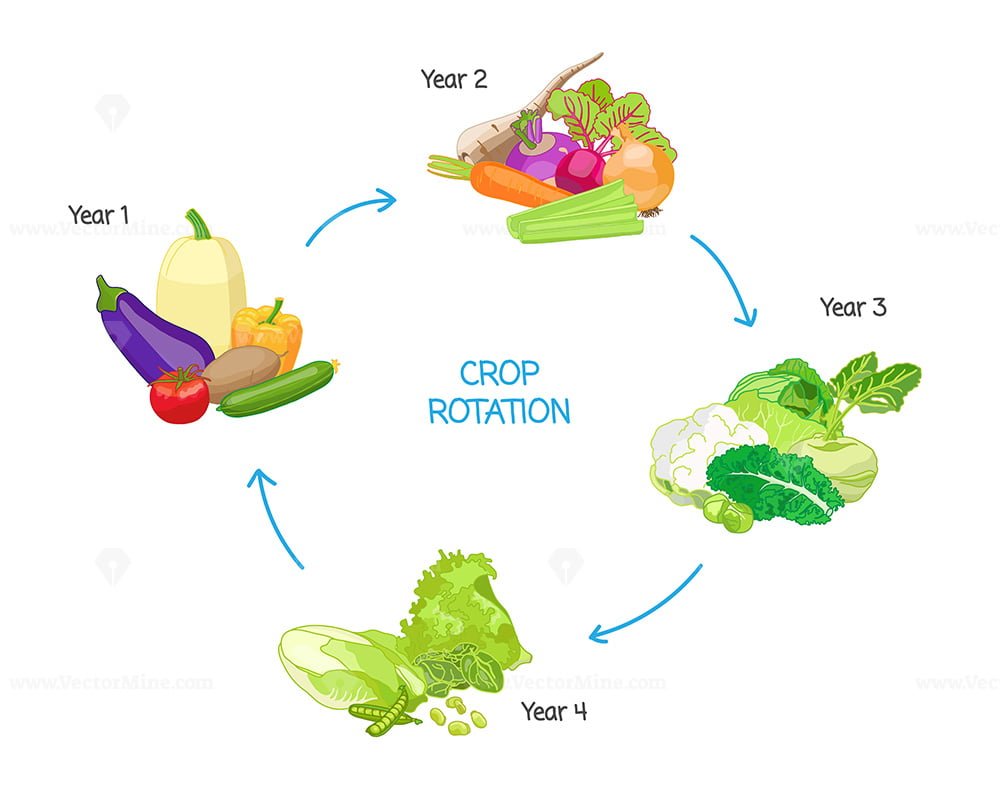
Source vectormine.com
Who Invented Crop Rotation?
Understanding the history of crop rotation can help us appreciate the importance of sustainable farming practices that ensure soil fertility, reduce pests and diseases, and increase crop yields. Crop rotation has been practiced for thousands of years, with different civilizations developing their techniques to adapt to their unique farming needs.
The Basics of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation involves changing the type of crops grown in a particular field over time to maintain soil health and fertility. This farming technique works by alternating deep-rooted and shallow-rooted crops, nitrogen-fixing and non-nitrogen-fixing crops, and different plant families that have varying nutrient requirements. By rotating crops, farmers can enhance soil structure, reduce soil-borne diseases and pests, conserve moisture, and improve yields. In essence, crop rotation mimics nature's diverse and complex ecological systems.
Ancient Crop Rotation Techniques
Ancient civilizations such as the Incas, Aztecs, and Greeks practiced crop rotation techniques to increase food production. The Greeks, for example, used a triennial rotation, where they planted wheat, barley, and legumes in a cycle. The legumes provided nitrogen to the soil, while wheat and barley were shallow-rooted crops. The Aztecs used a system known as the chinampas, which involved building rectangular gardens on small islands in shallow lakes. They planted maize, beans, squash, and other crops and regularly added organic matter to the soil to maintain its fertility.
Jethro Tull and the Agricultural Revolution
Jethro Tull was an English farmer who lived in the 17th and 18th centuries. He is widely credited with popularizing crop rotation during the Agricultural Revolution in Britain. Tull invented a horse-drawn seed drill that could plant seeds in neat rows and depths, which reduced seed waste and increased crop yields. He also recognized the importance of deep tilling, weeding, and hoeing to loosen soil and remove weeds, which previously had been done manually by hand.
Tull advocated for the use of legumes such as clover and turnips in crop rotation, which can restore soil nutrients and add nitrogen to the soil. Tull's ideas also led to the development of hybrid crops that were bred to grow faster, resist pests and diseases, and tolerate changing weather conditions. The improvements in crop yields were significant and helped to feed a growing population without using more land.
In conclusion, while we cannot pinpoint a single person who invented crop rotation, it is clear that many civilizations and agricultural pioneers played a role in developing and refining techniques that have been passed down from generation to generation. Today, crop rotation is one of the fundamental practices of sustainable agriculture and remains relevant in ensuring food security and environmental conservation.
The Science Behind Crop Rotation
Crop rotation is a farming technique that has been used for centuries. It involves planting different crops in a specific order over several years in the same field. The basic principle of crop rotation is based on the idea that different crops have different nutrient needs and deplete the soil of specific nutrients
The Benefits of Crop Rotation
Crop rotation has several benefits for the health of the soil and the crops. Firstly, it improves soil fertility by using different crops that have different nutrient requirements. Therefore, soil nutrients are replenished and not depleted. This leads to higher crop yields, as the soil is not overworked and does not become infertile. Secondly, crop rotation reduces soil erosion by planting crops that have different root structures, which helps to bind and improve the soil structure. Finally, crop rotation also reduces pests and diseases, as different crops attract different pests and diseases. Therefore, pests and diseases are less likely to become established and spread.
How Crop Rotation Works
The first step in crop rotation is to establish the order in which the crops will be planted. This order should take into account the nutrient needs of each crop, as well as any pests or diseases that may be present. The second step is to plant the crops in the same field in the specified order. Each crop will be grown for a specific length of time, depending on its nutrient requirements and the farmer's schedule.
The main idea behind crop rotation is simple. Different types of crops use different types of nutrients. Therefore, by rotating crops, you ensure that the soil is replenished with the nutrients that are required by each crop. For example, legumes are often used in crop rotation because they fix nitrogen in the soil. This nitrogen can then be used by other crops in the following years.
Modern Crop Rotation Practices
Modern farmers use scientific techniques to determine which crops should be rotated and when. Soil tests are conducted to determine nutrient levels, and computer programs are used to help farmers plan out their crop rotation schedules. The use of modern technology has led to greater yields and improved soil health.
Another modern practice is the use of cover crops. Cover crops are planted in between the main crops and help to improve the soil structure and fertility. They also help to prevent soil erosion, reduce weed growth, and attract beneficial insects. Cover crops are often legumes or grasses that are not harvested but are instead plowed under to add organic matter to the soil.
In conclusion, crop rotation is an important farming technique that has been used for centuries. It has several benefits for the health of the soil and the crops. Modern farming practices have made it even more effective, making it a popular and essential technique for farmers all over the world.
Crop Rotation and Sustainable Agriculture
Crop rotation is an agricultural practice that involves alternating the crops grown on a particular plot of land in sequential seasons. This practice has been used for centuries, with its origins traced back to ancient Rome and China. However, the exact identity of the person who first invented it is unknown.
Importance of Sustainable Agriculture
Sustainable agriculture is essential for the preservation of the earth's natural resources, particularly in the face of adverse climate changes. It helps to maintain and improve soil fertility and conserve water resources while reducing the negative impact on biodiversity and climate change by mitigating greenhouse gas emissions. Moreover, it sets the stage for healthy ecosystems, enhances farmer livelihoods, and provides for the adequate nourishment of society for generations to come.
Crop Rotation for Sustainable Agriculture
Crop rotation is a vital aspect of sustainable agriculture. Its practice involves rotating crops with different nutrient requirements to help restore soil fertility and reduce soil-borne pests and diseases. This practice also helps to prevent soil erosion, as crops with extensive root systems leave behind organic matter that helps to stabilize soil structure and prevent soil degradation.
By alternating crops, crop residues, and other organic matter, soil fertility improves, and the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides is reduced, which can cause significant environmental damage when used inappropriately. With time, pest populations beget reduced, leading to reduced pest damage, hence fewer pesticides are needed.
Crop Rotation and the Future of Agriculture
Crop rotation contributes to healthier and more ecologically responsible farming practices. As agriculture moves towards sustainability, crop rotation is likely to become more widespread. Studies show that crop rotation can increase productivity, reduce operating costs, and mitigate potential environmental harm caused by monoculture. As such, this practice should be encouraged through education and promotion campaigns that target farmers and the general public. This would undoubtedly aid in the global effort to reduce the rate of climate change and environmental degradation by working towards sustainable agriculture.
In conclusion, the importance of sustainable agriculture cannot be overstressed, and crop rotation is one of the key practices in achieving this. With proper implementation, it can help to improve soil fertility, reduce pests and diseases, reduce the use of chemical fertilizers and pesticides, and promote a healthier ecosystem. As such, crop rotation is a vital component of sustainable agriculture, and it has a significant role to play in the future of agriculture.